In today's digital age, the quality of images captured by cameras plays a crucial role in various industries, from smartphones to autonomous vehicles. Behind the scenes, a specialized group of professionals works tirelessly to ensure that the images we see are crisp, clear, and true to life. These experts are known as Camera Image Quality Tuning Engineers, and their work is essential in shaping the visual experiences we encounter daily.
Introduction to Camera Image Quality Tuning Engineering
Camera Image Quality Tuning Engineering is a field that combines technical expertise with artistic sensibility to optimize the performance of digital imaging systems. This discipline focuses on enhancing the output of camera sensors through careful calibration and adjustment of various parameters.
Overview of Camera Image Quality
Camera image quality refers to the overall visual fidelity and accuracy of images produced by a digital camera system. It encompasses various aspects such as color accuracy, sharpness, dynamic range, noise reduction, and low-light performance. Achieving high image quality requires a deep understanding of optics, sensor technology, and image processing algorithms.
Importance of Image Quality in Modern Technology
In an era where visual content dominates communication and decision-making processes, the importance of image quality cannot be overstated. From social media platforms to medical imaging, from security systems to space exploration, high-quality images are essential for:
- Accurate representation of reality
- Effective communication of information
- Enhanced user experiences in digital products
- Reliable data for machine learning and AI applications
- Critical decision-making in fields like healthcare and autonomous driving
As technology continues to advance, the demand for superior image quality grows, making the role of Camera Image Quality Tuning Engineers increasingly vital.
Roles and Responsibilities of a Camera Image Quality Tuning Engineer
Camera Image Quality Tuning Engineers are the unsung heroes behind the stunning visuals we encounter in our daily lives. Their work ensures that the images captured by various devices meet the highest standards of quality and accuracy.
Key Responsibilities
The primary goal of a Camera Image Quality Tuning Engineer is to optimize the performance of imaging systems. This involves a range of tasks and responsibilities:
Image Calibration
One of the most critical aspects of an Image Quality Tuning Engineer's job is calibrating camera systems. This process involves:
- Adjusting color balance to ensure accurate color reproduction
- Fine-tuning exposure settings for optimal brightness and contrast
- Calibrating white balance to adapt to different lighting conditions
- Optimizing focus algorithms for sharp, clear images
Quality Assessment
Engineers must continuously assess the quality of images produced by camera systems. This includes:
- Conducting thorough visual inspections of test images
- Using specialized software to analyze image characteristics
- Comparing output against industry standards and benchmarks
- Identifying and documenting any defects or areas for improvement
Tuning Camera Parameters
Based on their assessments, engineers adjust various camera parameters to enhance image quality:
- Modifying ISP (Image Signal Processor) settings
- Adjusting noise reduction algorithms
- Fine-tuning sharpening and detail enhancement processes
- Optimizing HDR (High Dynamic Range) performance
Collaboration with Cross-Functional Teams
Image Quality Tuning Engineers often work closely with other teams:
- Coordinating with hardware engineers to address sensor-related issues
- Collaborating with software developers to implement image processing algorithms
- Providing feedback to product managers on image quality improvements
- Working with user experience designers to ensure visual output meets user expectations
Required Skills and Qualifications
To excel in this field, Camera Image Quality Tuning Engineers need a unique blend of technical expertise and creative problem-solving abilities.
Technical Skills
- Proficiency in image processing techniques and algorithms
- Understanding of color science and color management systems
- Knowledge of optics and sensor technologies
- Familiarity with various image file formats and compression techniques
- Programming skills, particularly in languages used for image processing (e.g., Python, C++)
- Experience with image analysis tools and software
Educational Background
Most Camera Image Quality Tuning Engineers have:
- A bachelor's or master's degree in Electrical Engineering, Computer Science, or a related field
- Specialized coursework in image processing, computer vision, or digital signal processing
- Continuous learning through workshops, conferences, and industry certifications
Soft Skills
Beyond technical expertise, successful engineers in this field possess:
- Attention to detail and a keen eye for visual quality
- Strong analytical and problem-solving skills
- Excellent communication abilities to explain technical concepts to non-technical stakeholders
- Patience and persistence in fine-tuning and troubleshooting
- Creativity in developing innovative solutions to image quality challenges

Tools and Technologies Used in Image Quality Tuning
Camera Image Quality Tuning Engineers rely on a variety of specialized tools and technologies to perform their work effectively. These tools enable them to analyze, adjust, and optimize image quality with precision and efficiency.
Image Signal Processors (ISP)
Image Signal Processors are at the heart of modern digital imaging systems. They are responsible for processing raw sensor data and converting it into high-quality images. Camera Image Quality Tuning Engineers work extensively with ISPs to:
- Adjust color processing algorithms
- Implement noise reduction techniques
- Enhance image sharpness and detail
- Optimize dynamic range and exposure settings
Popular ISP platforms include:
- Qualcomm Spectra ISP
- Sony BIONZ X
- ARM Mali-C71 ISP
Engineers must be proficient in working with these platforms and understanding their capabilities and limitations.
Calibration Software
Specialized calibration software is essential for fine-tuning camera parameters and ensuring consistent image quality across different devices. Some commonly used calibration tools include:
- X-Rite i1Profiler: For color calibration and profiling
- DxO Analyzer: For comprehensive camera and lens testing
- Imatest: For image quality analysis and measurement
These tools allow engineers to:
- Create custom color profiles
- Measure and analyze various image quality metrics
- Generate detailed reports on camera performance
Testing Equipment
To accurately assess image quality, engineers use a range of specialized testing equipment:
- Light boxes and controlled lighting setups
- Color charts and test targets (e.g., X-Rite ColorChecker)
- Resolution test charts
- Spectrometers for precise color measurement
- High-resolution reference monitors
This equipment enables engineers to create standardized testing environments and obtain consistent, reliable results when evaluating image quality.
Job Market and Opportunities
The field of Camera Image Quality Tuning Engineering is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing importance of visual technology in various industries.
Current Job Openings
A quick search on major job boards reveals numerous opportunities for Camera Image Quality Tuning Engineers across different sectors:
- Smartphone manufacturers (e.g., Apple, Samsung, Google)
- Automotive companies developing advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS)
- Security and surveillance system providers
- Medical imaging equipment manufacturers
- Drone and robotics companies
Job titles may vary and include:
- Camera Image Quality Engineer
- Imaging Systems Engineer
- Camera Tuning Specialist
- Computer Vision Engineer (with a focus on image quality)
Industry Demand for Camera Image Quality Engineers
The demand for skilled Camera Image Quality Tuning Engineers is driven by several factors:
- Rapid advancements in smartphone camera technology
- Growing adoption of computer vision in autonomous vehicles
- Increasing use of high-quality imaging in medical diagnostics
- Expansion of augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) applications
- Rising consumer expectations for image quality in all digital devices
This demand is reflected in competitive salaries and benefits packages offered to experienced professionals in the field.
Career Progression and Advancement
Camera Image Quality Tuning Engineers have various paths for career advancement:
- Specialization in specific industries (e.g., automotive, medical imaging)
- Moving into leadership roles, such as Team Lead or Engineering Manager
- Transitioning into research and development of new imaging technologies
- Consulting or starting independent image quality assessment businesses
- Contributing to industry standards and specifications development
As the field evolves, opportunities for growth and specialization continue to expand, making it an exciting career path for those passionate about imaging technology.
TalenCat: Crafting the Perfect CV for Camera Image Quality Tuning Engineers
For camera image quality tuning engineers looking to showcase their specialized skills and experience, TalenCat CV Maker is an excellent tool to create a standout resume. This user-friendly platform offers tailored templates and AI-powered assistance to help you craft a professional CV that highlights your expertise in image processing, color science, and camera tuning algorithms.
Here's a step-by-step guide to creating your camera image quality tuning engineer resume using TalenCat CV Maker:
Step 1: After logging in, click the + Create Resume button to start a new resume tailored for your camera image quality tuning engineer position.

Step 2: Name your resume something relevant like "Camera Image Quality Tuning Engineer CV" and choose to create with an example for a head start.

Step 3: You'll now see the CV editor. Fill in your details, focusing on your experience with image processing algorithms, color calibration techniques, and camera sensor optimization. The right panel will update in real-time, giving you an immediate preview of your CV.

Step 4: Utilize TalenCat's AI-powered features to enhance your CV. The AI can suggest improvements to your content and help you highlight key skills specific to camera image quality tuning.
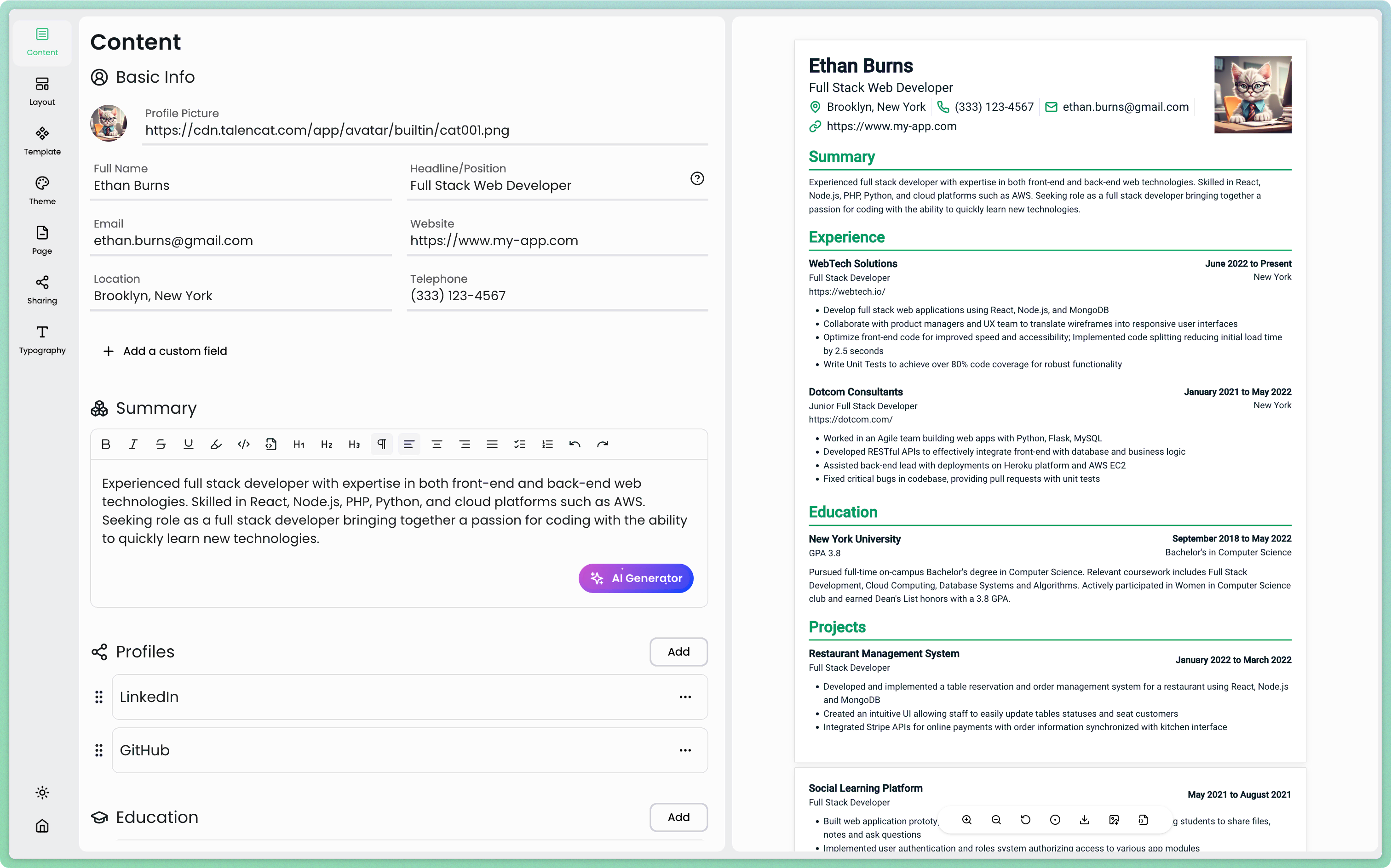
Once you've completed your CV, you can export it as a PDF or enable the online sharing feature to get a shareable link. This makes it easy to send your professional camera image quality tuning engineer CV to potential employers or colleagues in the imaging industry.
Remember to regularly update your CV with new skills and experiences in camera tuning algorithms, image quality assessment methodologies, and any relevant certifications or projects you've completed.
With TalenCat CV Maker, you'll have a polished, professional resume that showcases your expertise in camera image quality tuning, helping you stand out in this competitive field.
Case Studies and Real-World Applications
To better understand the impact of Camera Image Quality Tuning Engineering, let's explore some real-world applications and challenges faced by industry leaders.
Examples from Industry Leaders
Qualcomm
Qualcomm, a leading provider of mobile technologies, has made significant strides in camera image quality through its Spectra ISP technology.
Case Study: Qualcomm Snapdragon 888 Mobile Platform
The Snapdragon 888, released in 2020, featured an advanced Spectra 580 ISP. Camera Image Quality Tuning Engineers at Qualcomm worked on:
- Implementing a triple ISP architecture for simultaneous multi-camera processing
- Developing AI-based auto-focus, auto-exposure, and auto-white balance algorithms
- Enhancing low-light performance through advanced noise reduction techniques
Results:
- Ability to capture 120 photos per second at 12MP resolution
- Improved dynamic range in challenging lighting conditions
- Reduced motion blur in action shots
This case demonstrates how image quality tuning can push the boundaries of mobile photography, enabling smartphone cameras to rival professional-grade equipment.
Tesla
Tesla's Autopilot system relies heavily on camera-based perception, making image quality crucial for safe autonomous driving.
Case Study: Tesla Vision
In 2021, Tesla announced a shift towards a camera-only approach for its Autopilot system, removing radar sensors from new Model 3 and Model Y vehicles.
Challenges faced by Camera Image Quality Tuning Engineers:
- Ensuring consistent performance across various lighting and weather conditions
- Optimizing image quality for both near-field and long-range object detection
- Balancing image processing requirements with real-time performance needs
Solutions implemented:
- Development of custom neural networks for image enhancement and object recognition
- Fine-tuning of camera parameters to maximize useful information capture
- Implementation of advanced HDR techniques to handle high-contrast scenarios (e.g., driving into sunlight)
Results:
- Improved object detection and classification accuracy
- Enhanced performance in challenging weather conditions
- Reduced system complexity and cost by eliminating radar sensors
This case highlights the critical role of image quality in safety-critical applications and the need for continuous optimization.
Challenges Faced in Camera Tuning
Camera Image Quality Tuning Engineers face numerous challenges in their work, balancing technical limitations, user expectations, and practical constraints.
Manual vs. Automated Tuning Processes
One of the ongoing debates in the field is the balance between manual and automated tuning processes.
Manual Tuning:
- Allows for fine control and artistic input
- Can address subtle image quality issues
- Time-consuming and potentially inconsistent
Automated Tuning:
- Offers faster processing and consistency across devices
- Can leverage machine learning for continuous improvement
- May miss nuanced issues that human experts can identify
Many companies are adopting hybrid approaches, using automated systems for initial tuning and manual fine-tuning for final adjustments. This combination aims to leverage the strengths of both methods while mitigating their weaknesses.
Other common challenges include:
- Adapting to rapidly evolving sensor technologies
- Meeting diverse image quality requirements across different markets and user preferences
- Balancing image quality with power consumption and processing speed
- Ensuring consistent performance across a wide range of shooting conditions
Addressing these challenges requires continuous learning, creativity, and collaboration across different engineering disciplines.
Future Trends in Camera Image Quality Tuning
As technology continues to evolve, the field of Camera Image Quality Tuning Engineering is poised for significant advancements. Understanding these trends is crucial for professionals looking to stay at the forefront of the industry.
Advances in Technology
Several technological developments are shaping the future of image quality tuning:
Computational Photography
- Increasing use of multi-frame capture and processing
- Advanced HDR techniques for extreme dynamic range
- Focus stacking for extended depth of field
Sensor Innovations
- Larger sensors with improved light-gathering capabilities
- Stacked CMOS sensors for faster readout and reduced rolling shutter
- Quad Bayer and other novel pixel arrangements for enhanced low-light performance
8K and Beyond
- Tuning for ultra-high-resolution capture and display
- Balancing detail preservation with efficient compression
Multi-Camera Systems
- Optimizing image quality across multiple lenses and sensors
- Seamless blending of images from different cameras
Real-Time Ray Tracing
- Integration of ray tracing techniques for more realistic image rendering
- Potential applications in AR/VR and computational photography
Role of Artificial Intelligence in Tuning
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is set to play an increasingly important role in camera image quality tuning:
Automated Tuning Processes
- AI-driven systems for initial camera calibration and tuning
- Continuous optimization based on user behavior and preferences
Scene Understanding
- AI algorithms for intelligent scene recognition and adaptive processing
- Contextual adjustments based on subject matter and shooting conditions
Neural ISPs
- Development of AI-powered Image Signal Processors
- Potential for more flexible and adaptable image processing pipelines
Personalized Image Quality
- AI systems that learn individual user preferences
- Customized image processing tailored to specific users or use cases
Predictive Maintenance
- AI-based monitoring of camera system performance
- Early detection of potential image quality issues or hardware degradation
As these technologies mature, Camera Image Quality Tuning Engineers will need to adapt their skills and workflows to incorporate AI-driven tools and techniques effectively.
Conclusion
Camera Image Quality Tuning Engineering is a dynamic and crucial field at the intersection of technology and visual arts. As we've explored throughout this article, these professionals play a vital role in shaping the visual experiences we encounter in our daily lives, from the photos we take with our smartphones to the safety systems in our vehicles.
Summary of Key Points
- Camera Image Quality Tuning Engineers are responsible for optimizing the performance of digital imaging systems through calibration, assessment, and parameter adjustment.
- The field requires a unique blend of technical skills, including knowledge of image processing, color science, and optics, along with creative problem-solving abilities.
- Tools and technologies used in the field range from specialized Image Signal Processors to calibration software and testing equipment.
- The job market for Camera Image Quality Tuning Engineers is growing, driven by advancements in smartphone technology, autonomous vehicles, and other imaging-dependent industries.
- Real-world applications, as seen in case studies from companies like Qualcomm and Tesla, demonstrate the critical impact of image quality tuning on product performance and user experience.
- Challenges in the field include balancing manual and automated tuning processes and adapting to rapidly evolving technologies.
- Future trends point towards increased integration of AI in tuning processes and the need to optimize for new technologies like computational photography and multi-camera systems.
Final Thoughts on the Future of Camera Image Quality Tuning Engineering
As we look to the future, the role of Camera Image Quality Tuning Engineers will continue to evolve and grow in importance. The increasing reliance on visual data across industries, coupled with advancements in AI and computational photography, will create new challenges and opportunities for professionals in this field.
To stay relevant and effective, Camera Image Quality Tuning Engineers will need to:
- Continuously update their skills and knowledge to keep pace with technological advancements
- Develop expertise in AI and machine learning as these technologies become more integrated into image processing workflows
- Balance technical optimization with an understanding of human perception and user experience
- Collaborate effectively across disciplines, working with hardware engineers, software developers, and product designers
The future of Camera Image Quality Tuning Engineering is bright, with the potential to shape how we see and interact with the world around us. As visual technology becomes increasingly central to our lives, the expertise of these professionals will be crucial in ensuring that the images we capture and view are not just data, but accurate, beautiful, and meaningful representations of our world.




